|
Glossary
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
Z
>
full image
A
back
to the index
Absolute
humidity
Actual amount of water vapour in a unit
volume of air (ISO).
Acid
free paper
Papers which contain no free acid and have a pH value of 7.0 or greater. It is
suggested for preservation process.
Adhesive
binding
See perfect binding
All across sewing
see All along sewing
All on sewing
see All along sewing
All along sewing
In bookbinding by hand, a
method of sewing a book by passing the thread in and out and over the cords or
tapes along the whole lenght of the inside fold of each section. The thread
goes "all along," inside the fold of the section—that is, from
kettle stitch to kettle stitch of each successive section, one complete length
of thread for each section.
Assuan
A quality and expensive book cloth made from cotton or linen.
It is ill advised for consulter books because of its delicacy.
Anchorage
Term usually used in bookbinding to indicate the different systems
to fix the book block to the cover.
The attachment may be direct when the junction of the book block to the covers
is done contemporaneously to the sewing of the papers: lashing to file,
oriental sewing, etc.
The attachment may be indirect when the book block is sewed separately from
the cover, using sewing supports. The indirect attachments may be done by
folders, passing nerves, incart-boarding lacing-in, split.
B
back
to the index
Back
The edge of a book along which the leaves or sections are bound together.
However, the same word is used to describe the outer cover wich covers the
back of the book. It generally bears the
title, author, name of the publisher (when an
edition binding), and (in a library) frequently a location (classification)
number, or a symbol of some kind. Also called backbone or
shelfback.
Backbone
see Back
Backing
see Spine
linings
Back corner
The cutting away of a small triangular pieces of the head and tail edges of
the borads of a book at the joints. the purpose is to relieve the strain on
the joints of a book when the covers are opened.
Band
See cord.
Bifolium
A pair of conjoint leaves.
Board
A generic term for the pieces of wood, metal, or metal-edged wood used to
assist in gripping books while in process of being bound. Such boards are
used in pressing, backing, bundling, gilding, trimming, and other operations. Wooden table was used as a
dish, particularly in the vellum codes.
Bolts
The folded edge at the head, tail, or
fore edge of a section of an unopened
book. (see also cut and deckle edge)
Book
See volume.
Bookbinding
The finished work resulting from the processes involved in binding a book,
that is securing the leaves or sections of a publication so as to keep them in
proper order and to protect them.
Even the style in which a book is bound, e.g., edition binding, library
binding, etc.
Book block
The text block together with the endpapers and others materials added by the binder
before casing in to a hard cover.
Book corner
Protective caps for the corners of book covers, sometimes made of leather, but
also of metal or the same material that covers the book. Also called "corners."
See even corner.
Book
jacket
see Dust jacket
Bookmark
Any paper or other material used in marking a place in a closed book for
future reference. Bookmarks are frequently decorative, carrying advertisements
or commemorative illustrations.
Border
See Fore edge
Bowed
plate
See buckling.
Buckling/bowed
Loss of the original shape by distorsion
of the plates or the axis of the cover, in
one or more planes
More or less accentuated bend of the plates or the axis of the cover.
Buckram
A book cloth made from cotton or linen, usually the former, and closely woven,
occasionally with a double warp. It is filled or coated and calendered to give
it a smooth finish which blocks well and is reasonably durable. The material
used to fill the interstices and/or cover the base fabric is usually pyroxylin,
but it may be starch, china clay, clay, or other nonfibrous material.
C
back
to the index
Case
See square.
Case binding
A method of bookbinding in which the case (covers) of the book is made
separately from the book (the text block and endpapers) and later attached to
it by gluing the board papers of the text block to the inside of the boards
of
the case.
Chinese
or japanese sewing
see oriental sewing.
Cold printing
See dry
printing
Compensation
In tying the operation with which, during the sewing of the
signature, the empty spaces between the cords of the seam are filled up with
passages of strand. Often used in the flexible sewing.
Cord
The cotton, hemp, linen or silk cords or bands, of varying thicknesses, which
extend across the backs of the gathered sections and are used in
sewing books
through the folds. Cords may be single or double ,
recessed, passing or lacing-in.
Core
Stripe of various materials (papyrus, leather, string, etc) awrapped around the strand of the
headband. (see also cord)
Corner
The juncture of the two edges of a book cover at the fore edge and head and
tail.
Types of corners include the library
corner, round
corner, and square
corner.
(See also tip)
Cover
It’s a more generic term than case, used to imply any protective covering
used on the outside of a book. Covers may be built onto the book (including
laced-on boards and tight-back leather bindings), can be built separately
from the textblock (including most modern cases), or be of simple, paperbach
construction.
Cut
To trim the edges of books.
D
back
to the index
Deckle
edge
The edges of a newly printed book which have not been cut or trimmed. Typical
of the ancient
hand made papers (see also fore edge)
Division
It is a part of the spine comprised between the bands. After
the back coating it became panel.
Dog-eared
A book or other publication having one or more corners of the leaves turned
down, generally by readers.
Spine stamplettering pattern
Decoration of leather or papyrus covers resorting to metallic pins, usually
known as irons; these are used hot, without coloured films. Letterpress
includes printing from raised type, halftone, or woodcuts on a platen,
cylinder, or rotary press printing
Dust
jacket
A wrapper originally used to protect
the covering material of the book from soiling or other damage, but now also
used for promotional purposes. It may be plain, printed, or illustrated, and
is flush with the covers of the book at head and
tail, but folded over the
fore edge of both covers. It is usually detachable. Modern book jackets are
often very elaborately designed and are frequently printed in color. Also
called "book wrapper," "dust cover," "dust jacket,"
"dust wrapper," "jacket," and "wrapper."
E
back
to the index
Edition
binding
The binding of a book in identical style, usually in mass production in
large quantities. Also called Publisher's Binding
Endpapers
Papers or leaves placed at the end and beginning of the
book to protect the
text and to act as part of the attachment between the book and the cover
boards. Most commonly, an endpaper consists of an outer pastedown and at least
one flyleaf.
Environmental
pharametres
The surrounding conditions or forces that influence or change books or other
archival materials, and which include: 1) the entire climatic and biotic
factors that act upon materials and ultimately determine their permanence,
or lack of i (temperature: between 18° and 20°C;
relative humidity: between 45% and 65%;
light: to limit within the 50 lux.); or 2) the aggregate of use, misuse,
or nonuse that influence the permanence of materials.
F
back
to the index
False
raised band
The imitation raised cords (bands) found on some books. They consist of
narrow strips of leather (or other material, e.g., vellum) attached directly
to the hollow of the cover. They are generally glued to the hollow of the
spine, are sometimes used to
give the impression of flexible
sewing . (see also False raised back)
False
raised back
Such books are generally sewn on sawn-in cords or in the case of a tight back binding, directly
to the spine of the book. The false bands stand out in imitation of a book
sewn on raised cords. (see also False raised
band)
Flat back
The back of a book which has not been rounded and backed before the
boards
are attached is called Flat back. A back glued directly to the book is
called tight back or fast back. The opposite of round
back.
Flexible binding
A style of binding in which the sewing allows the book to open flat.
Flexible sewing
A method of sewing the sections of a book to cords or bands which are above
the backs of the sections and rest against them, as opposed to being recessed.
Flyleaf
see Endpapers
Folder
One sheet of paper folded to make two or more leaves but not stitched or cut.
Folding
see section.
Fore
edge
Front or opposite part to the spine. Even the top
edge of a bound
book, called Head, or the bottom edge of a bound book, called
tail.
G
back
to the index
Gathering
See Section.
Glue
binding
See Perfect binding.
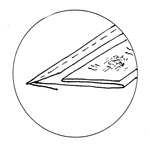
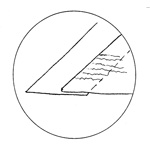
Guard
A strip of cloth or paper pasted around or into a section of a book so as to
reinforce the paper and prevent the sewing thread from tearing through. A
guard may also be required for leaves or plates that have become frayed or
detached at the inner edge.
H
back
to the index
Half
binding
A style of binding in which the spine and part of the side of the book, as
well as the four corners, are covered with one kind of material, e.g., leather,
cloth, etc., and the sides with another material, e.g., cloth or paper.
Head
The top edge of a bound book. (See even
fore edge).
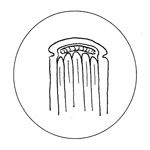
Headband
A functional and/or ornamental band at
the head and tail of a book between the
sections and the spine covering, which
projects slightly beyond the head and tail. Originally, the headband consisted
of a thong core, similar to the bands on which the book was sewn, around which
the ends of the threads were twisted and then laced into the boards of the
book. Today, however, the headband is much simpler and is usually made of
colored silk sewn to the book or simply attached after the volume has been
forwarded. In edition binding they are almost always manufactured separately
and then attached, while in library binding they have been replaced for the
most part by a length of cord around which the covering material is rolled at
both head and tail.
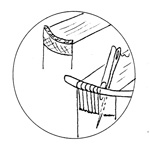
Headcap
The leather covering at the head and tail of the
spine of a book, formed by
turning the leather on the spine over the head and tail and shaping it.
I
back
to the index
Inlay
A strip of kraft or other
relatively stiff paper, used to stiffen the spine area of the
case of a
library binding. Edition bindings generally do not have inlays.
Inserts
An additional printed leaf or leaves, circular, etc., placed between the
leaves of a book, pamphlet, newspaper, etc. (see also plate)
J
back
to the index
Japanese
paper
A very thin, strong paper made in Japan from long-fibered stock. It is a very
versatile paper, and depending on the thickness, may be used for mending torn
book leaves, for the overall lining of paper as reinforcement, for reinforcing
the folds of sections, or for mending hinges. It is for the most part handmade.
Also called "long-fibered Japanese tissue."
K
back
to the index
Kettle stitch sewing
The sew stitches are situated between the
highest cord and the top headband and between the lowest cord and the feet
headband, with the purpose of wrapping the seam of the signature. The kettle
stitch is used to fasten one signature to another.
L
back to the
index
Label
A square or rectangular piece of leather, cloth, or paper, usually of a
different color from that used for covering, and attached to the spine, or (occasionally)
the upper cover of a book. Labels display the title of the book, the volume
number (if any), the author's name and the date of publication.
Lacing-in
The process in craft bookbinding of attaching the boards to the
text block
by passing the bands or cords on which the book is sewn through holes
punched or cut into the boards. The bands are first frayed out and moistened
with paste and then passed through the holes or slots.
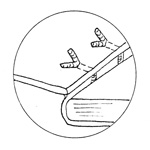
Lacing-in cord
See lacin-in.
Leaf
Single sheet of paper or half of folder a sheet of paper. Each side of the
leaf is a page. Usually the odd page is called recto and the even page is
called verso.
Light
see Environmental parameters
Lignin
An organic substance, forming the essential part of woody fibre.
It’s function is
to glue the fibres to the cellulose. Paper containing lignin degrades if exposed to the
light, to
high humidity or hot temperature. That's why paper turns to yellow.
Lining
Cotton, muslin, gauze, ctash, paper and
other materials used to reinforce spines fo library bound books. Lining
provides the means for a firm connection
between text block and cover and
gives shape and firmness to the binding.
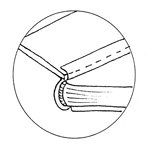
Lock-stitch
A sewing-machine stitch, in which
two threads are locked firmly together.
Lux
Light measurement unit.
M
back
to the index
Methylcellulose
Cellulose methyl ether, produced by treating cellulose from wood or cotton
with an alkali, such as sodium hydroxide, followed by methyl chloride. The
resulting product is a white granular solid, soluble in cold water but
insoluble in hot water. It is used as a thickening agent for aqueous
preparations and as a substitute for natural gums, and particularly as a
stabilizer in emulsions. It has also been used to greaseproof paper and as an
additive in adhesives to increase film strength, flexibility and adhesion.
N
back
to the index
Neutral
adhesive tape
An acid free paper tape. Recommended for
repairing joints, hinging, and mending damaged edges
of documents and book pages. Free from wood pulp and acid. Buffered with
calcium carbonate.
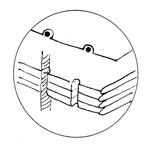
Notching
The
process of drilling the external borders of the leaves to receive the
cords.
This technique is not particularly resistant.
O
back
to the index
Obverso
See recto.
One
on and two off point
A method of making a hollow in which a strip of paper is cut three times the
width of the back of the book; the middle width is glued to the spine, the
two end widths fold over the middle are glued to each other.
Oriental sewing
Also known as chinese/japanese. Horizontal sewing method done on the whole
body of pages, it may comprise also the cover, the method consist on creating
small holes in the left side of the pages where the string will pass. In this
way you have a glue-free tying.
P
back
to the index
Page
One side of a leaf.
Panel
Part of the spine between the bands.
Panel
stamp
A relatively large block of
metal or wood, usually the former, engraved intaglio, and used to impress a
design on the cover of a book. Although little used today, the panel stamp
dates back perhaps 700 years or more.
Paper
see Leaf
Paperback
A book generally defined as a flat back book with a paper cover that is
usually, but not always, of a heavier stock than that used for the leaves of
the publication itself.
Passing
cord
Saying also threaded nerve that it passes through the blanket, visible to the
outside, in order to allow the anchorage of the blanket to the body of the
book.
Passing
in cord
See notching.
Paste-down
The inner part of the board. The anterior one is the inner part of the
anterior dish and the posterior one is the inner part of the posterior dish.
Perfect
binding
It’s a typical modern
lying executed gluing single pages to the back using a special glue, usually
hot. After the book’s opened a few times, the pages are detached easily.
Ph
A number expressing the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
The hydrogen-ion concentration of a solution may also be expressed in terms of
its pH, which is defined as the negative logarithm to the base ten of the
hydrogen-ion concentration. In aqueous solutions, neutrality is the condition
that exists when the concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions are
equal. At 25° C., neutrality occurs at a pH of 7.0, which is the pH value of
pure (distilled) water when condensed hot and shielded from contact with
atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Ph is important because the presence of acid(s) in ink, leather, paper, etc.,
has or can have, a deleterious effect on such materials. As a decrease of pH
means a logarithmic increase in acid concentration, levels of concentration
below pH 5.0, or under certain circumstances, even 6.0, become important.
Conversely, although not as serious a problem, a high concentration of
hydroxyl ions, corresponding to a pH of 10.0 or above, can lead to serious
oxydization of cellulosic materials.
Plate
An illustration printed separately from the text of the book, often on a
different type of paper. Plates may be bound into a book, tipped onto a blank
leaf (or a leaf bearing a printed caption), loose in a pocket or portfolio, or
bound in a separate volume. Plates are not generally included in the
pagination of the book. (see also Inserts)
Pocket
It is positioned at the end of the book and it is used to contain insert.
Polyethylene
Name
of polymeric substances prepared from derivatives of ethylene.
Plastic material obtained in order
to polymerize ethylene.
Printing cover
See edition binding.
Prop
Seam’s prop:it is a generic term
to indicate the seam’s underlying structure.(tape,sewing on tapes, cords,..)
Writing’s prop: it is a generic term to indicate any type of materials
like paper, vellum, papyrus.
Q
back
to the index
Quadrant
One of the rigid elements of
the cover .They could be in cardboard, or anciently, in more layers of
papers or parchment or wood. (see also Board)
R
back
to the index
Raised
band
The cords or thongs on
which the sections of a book are sewn. The cords are seen as ridges across the
spine of the covered book. (see also flexible sewing).
Rebinding
method
The more-or-less complete
rehabilitation of a worn and/or damaged book, the minimum amount of work
involving resewing and the attachment of new covers. (see also Bookbinding)
Recessed Cord sewing
A method of sewing a book by hand
which involves cutting grooves into the spine of the
gathered sections and recessing the cords
into those grooves. A single lenght of thread is carried from kettle
sticht, as in flexible sewing, but passes
across the cords instead of encircling them.
Recto
The first side of a printed or ruled sheet as distinct from the verso. The
right-hand page of an open book or manuscript, usually bearing an odd page
number.
Relative
humidity
Relations between absolute
humidity and saturation humidity. It is expressed in percent. The optimals
values, to conserve the books and the paper’s document and the vellum is
comprised between the 45% and the 65%.(see also Environmental
parameters).
Reversible
Capable of reversing, that is the fact, or action, of reverting or returning
to a primitive condition. referred to preservation or binding method.
Reversible adhesive tape
see Neutral
adhesive tape
Round
back
A book which has been shaped during the binding process to give it the
familiar convex spine. An arc of about
one-third of a circle.The opposite of Flat back.
Rope
The cotton, hemp, linen
or silk cords or bands, of varying thicknesses, which extend across the
backs of the gathered sections and are used in sewing books through the
folds. They are either sunk into saw cuts in the sections. (see also Cord)
S
back
to the index
Saturation
humidity
Maximum water-vapour
amount contents in a cubage air. (See also Environmental
parameters).
Square
The edges of the case that extend beyond
the text block at the head, tail, and fore
edge, and protect it.
Section
Number of folded leaves gathered together amd treated as a unit for
binding purpose.
Sewing
To attach and put together the leaves or signatures, to create the text block. The stitching may be without support or
with support with different techniques.
The most
important without support are:singer sewing, Kettle stitch sewing,
whip stitch, stitching, simple
eight seam, oriental.
The most important with support are:
sewing on tapes, sewing on cord,
simple point, one one and two
off sewing, notching, all
along sewing, wowen
point.
Sewing
on cord
Seam done using a support, usually a rope; the cord may be single or double;
the seaming string enters in the centre of the signature and goes out in
the back so it can embrace the support and form an open eight.
Sewing
on tapes
Seam done with a support of
cotton tape or duck, passing the
string inside the brochure and in
correspondence with the thread, the string must block the support without
wrapping it.
Shelfback
see Back
Shelf
mark
Shelf mark: it is a group of number
or letter. It show the position of the book in the library.
Brochure’s shelf mark: numbers or letters at the lower margin of
the paper; they will help the tier.
Signature
see Section
Simple eight point
See Simple eight seam
Simple eight seam
Also known as eight. Very simple sewing method, it’s done only on one
brochure passing the string inside it, embracing it in the place where the
pleat is.
Simple point
Seam in which the thread it exits on a side of the support and re-enters
embracing it.
Singer sewing
Industrial way of sewing
done with no supports, just using sewing string.
Single Paper
see
Leaf
Spine
see also Back
Spine
linings
The process of reinforcing the spine of
a sewn book, after gluing-up, rounding and backing, and before covering or
casing-in. The purpose of lining the spine is to support it and to impart a
certain degree of rigidity, while still maintaining the necessary
flexibility for proper opening; consequently the weight and stiffness of the
spine lining material is of considerable importance.
Splitting
Split
Technique of preparation of the quadrants
forms to you from cardboards of various grammatura, that heavier outside, that
inside glue on the back of the other, more light .The two cardboards are glue
on all the surface to you except the part in correspondence of the spirits of
last seam. These are inserted and glue exactly in the split (fissure) that it
must have one depth of approximately 4 cm.
Stirrup
see also Inlay
Stitch
A movement in sewing. Each
of the movements of a threaded needle in and out. The portion or loop of
thread or yarn left in the fabric as a result of this movement.
Stitching
Seam usually made on single papers or tables; it is a flat seam, the thread passes on the back of the papers in
visible and equal points; it may be simple or double. It’s a
nineteenth-century technique non appropriate to the conservation because the
papers usually tear in correspondence to the thread.
See Sewing
T
U
back to the
index
Tail
The bottom edge of a bound book. (See even Fore edge)
Tape
A strip of cloth, generally of cotton ribbon of neutral colour , used as a locking
up lace.
Temperature
Matter’s propriety. It is one of the
environmental parameters.
To prevente the
chimic, physic, biologic degradation of books, vellum and paper’s
document it is necessary a room-temperature comprised between 18° and 20° (see also
environmental parameters).
Text block
A gathering of printed or
written leaves thet may be or have been bound, excluding all
paper to be added
by the bookbinder such as the endpapers.
Thermo-hygrograph
Instrument for measuring Relative humidity.
Thread
A fine cord composed of the fibres or filaments of flax, cotton, wool, silk,
etc. spun to a considerable length.
Threaded
nerve
See passing nerve
Tip
See corner
Tipping
in
The attachement of one leaf to another, e. g., in a book by means
of a narrow strip of adhesive along one edge of the leaf.
Title
page
The recto of the second leaf of a book displaying the
name of the author, the full title, the edition, the publisher and the date of
publication or printing.
Tome
Each of the separate volumes which
compose a literary work or book; rarely, one of the largest parts or sections
of a single volume.
Trim
tab
See lining.
V
back
to the index
Verso
It is the back of the paper opposite to
the recto. It is represent with a “v” and sometimes with a “b”. It
coincides with the par number of the pages.
Verso of a carbon-tissue: the disposition of cellulose fiber determine the
flexibility of bracket and the consequence dilatation.
Volume
A collection of written or printed sheets bound together so as to form a book;
a tome.
W
Z
back
to the index
Warm printing
See Panel
stamp
Warped
volume
See notching.
Wowen
point
Seam in which the thread, after to be usito on a side of the support, it
overlaps the feature of thread of the previous issue and re-enters to the
other side of the support.
Whip
stitch
An overcast stitch.
(Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books. A Dictionary of Descriptive
Terminology. Matt T. Roberts and Don Etherington
Drawings by Margaret R. Brown. <http://palimpsest.stanford.edu/don/toc/toc1.html>
1996)
(Glossary of archive
preservation terms. English with equivalents in Spanish, German, Italian and
French. International Council on Archives: Committee on Conservation and
Restoration, 1985.)
(ANSI/NISO/LBI Z39.78-2000)
(ISO 5127:2001)
|